
Hunting for Real-Life Example
On August 2, 2024, Instagram was blocked in Turkey following a disagreement over content moderation. Immediately, users sought alternative methods to regain access, including changing DNS settings and relying on VPN services. While VPNs are a popular choice for bypassing such restrictions, cybersecurity professionals have consistently highlighted the dangers, especially when using unreliable VPN providers. This environment has allowed cyber attackers to take advantage of the increased demand for VPNs by distributing malware under the guise of legitimate VPN applications, putting users at significant risk.
To identify a real example of this threat, we can conduct a quick hunt on VirusTotal by crafting a query that targets malicious APK files. The search should focus on files first detected within the last seven days, containing the keyword vpn and initially submitted from Turkey. The following query will be used:
1
type:apk positives:10+ name:"*vpn*" first_submitter:tr fs:7d+
Running this query reveals an APK file named turbo-vpn-4-1-1-1.apk submitted from Turkey on 2024-08-08 at 14:44:59, and flagged as malicious by 18 out of 67 antivirus engines. This detection rate indicates a significant likelihood that the file is indeed harmful.
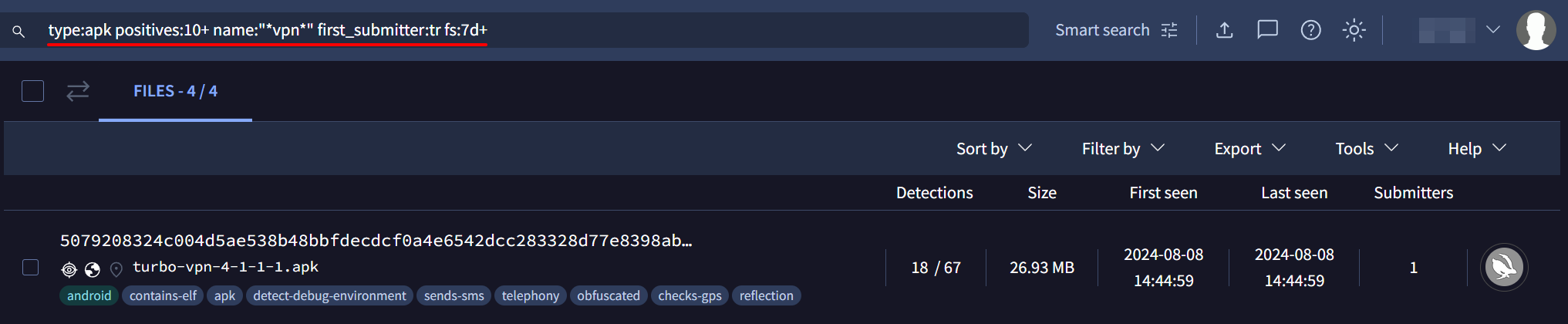
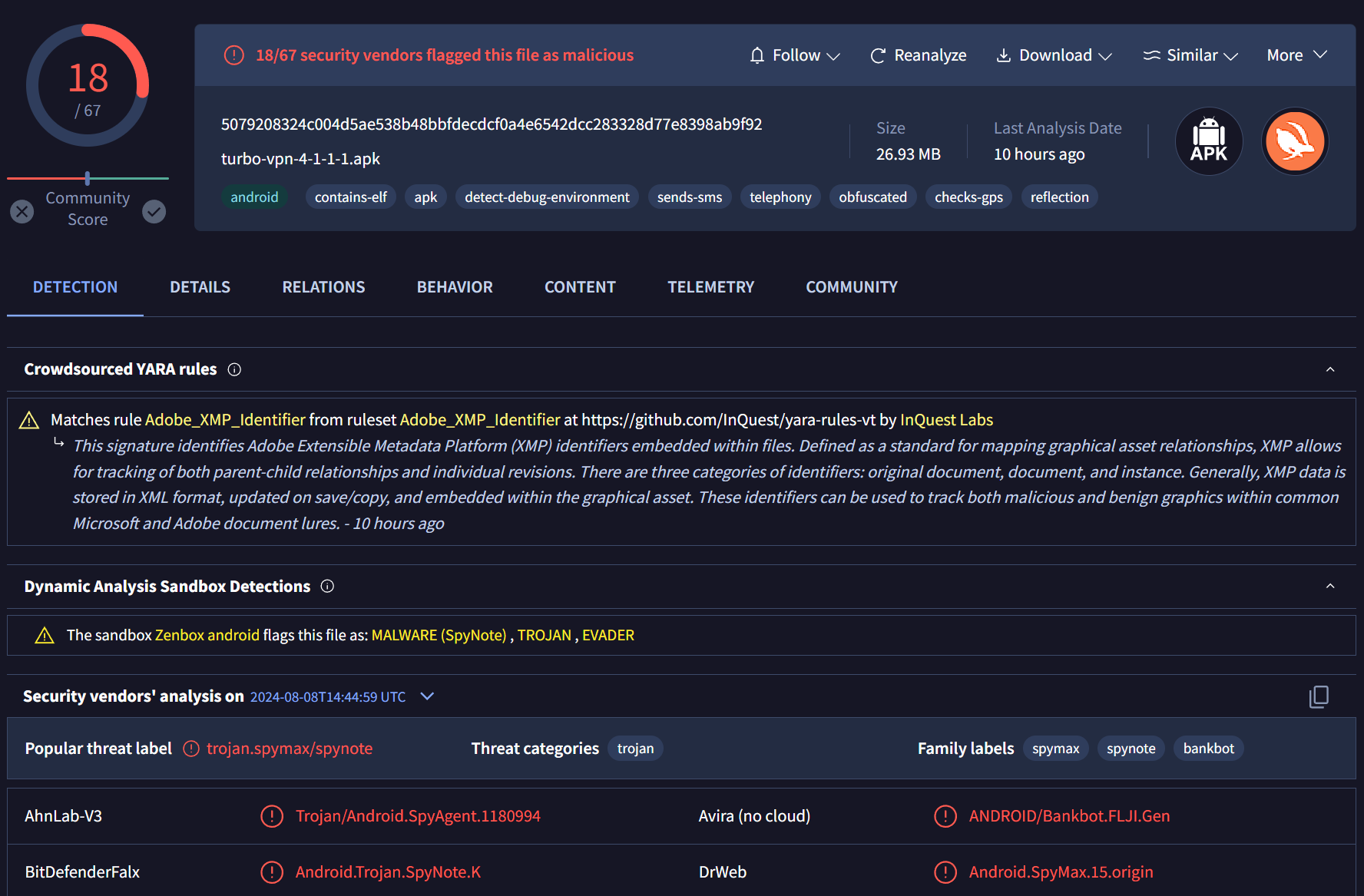
Antivirus engines recognized this file as Spynote Android malware, a well-known remote access trojan (RAT) that grants attackers full control over the infected device. Spynote is capable of stealing personal data, such as SMS messages, contacts, and call logs, and can even remotely activate the device’s microphone and camera. Its comprehensive spying capabilities make it a severe threat to user privacy and security.
Technical Analysis: An Overview
In this section, we will not be conducting an exhaustive technical analysis of the Spynote malware, as it has already been extensively covered in numerous research articles. Instead, our focus will be on a specific aspect of the sample: how the threat actor injected Spynote into the Turbo VPN application.
We’ll begin by decompressing the APK to identify the injected component—specifically, a malicious activity within the app—and then proceed to extract the C2 address used by the malware. For more detailed technical analysis of Spynote, you can check the references provided.
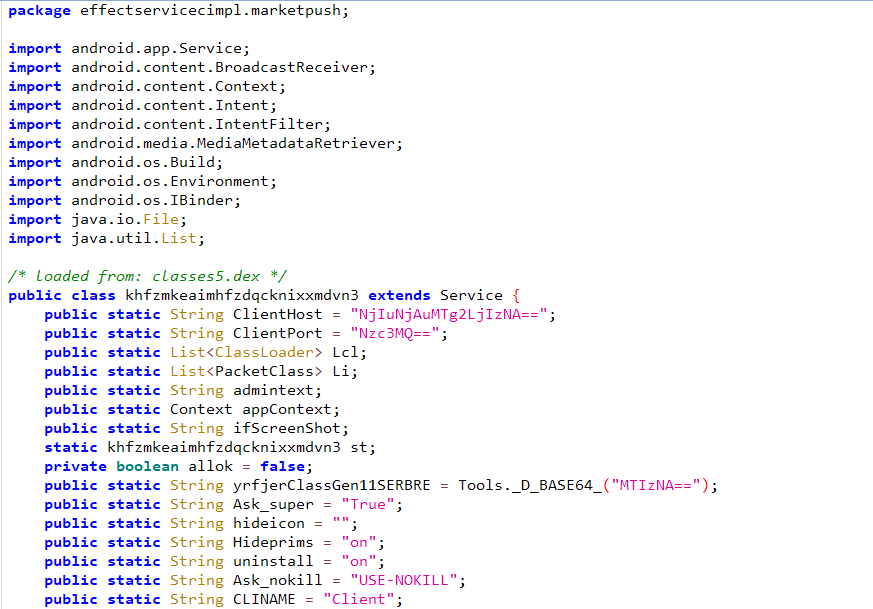
Upon decompressing and decompiling the APK file with JADX-GUI, we discovered multiple references to effectservicecimpl.marketpush and its associated obfuscated functions. These findings indicate that this component is integral to the app’s malicious activities, potentially serving as a gateway to execute the malware’s commands or communicate with the C2 server.

Within the effectservicecimpl.marketpush component, we found Base64 encoded strings in the service class “khfzmkeaimhfzdqcknixxmdvn3” that correspond to the C2 server’s address and port. Decoding them shows that the malware connects to a C2 server at 62.60.186.234 via port 7771.
By searching the identified IP address in VirusTotal and exploring its related files, we found another malicious file named build.exe / Steanings.exe which has been flagged as the Redline Stealer.
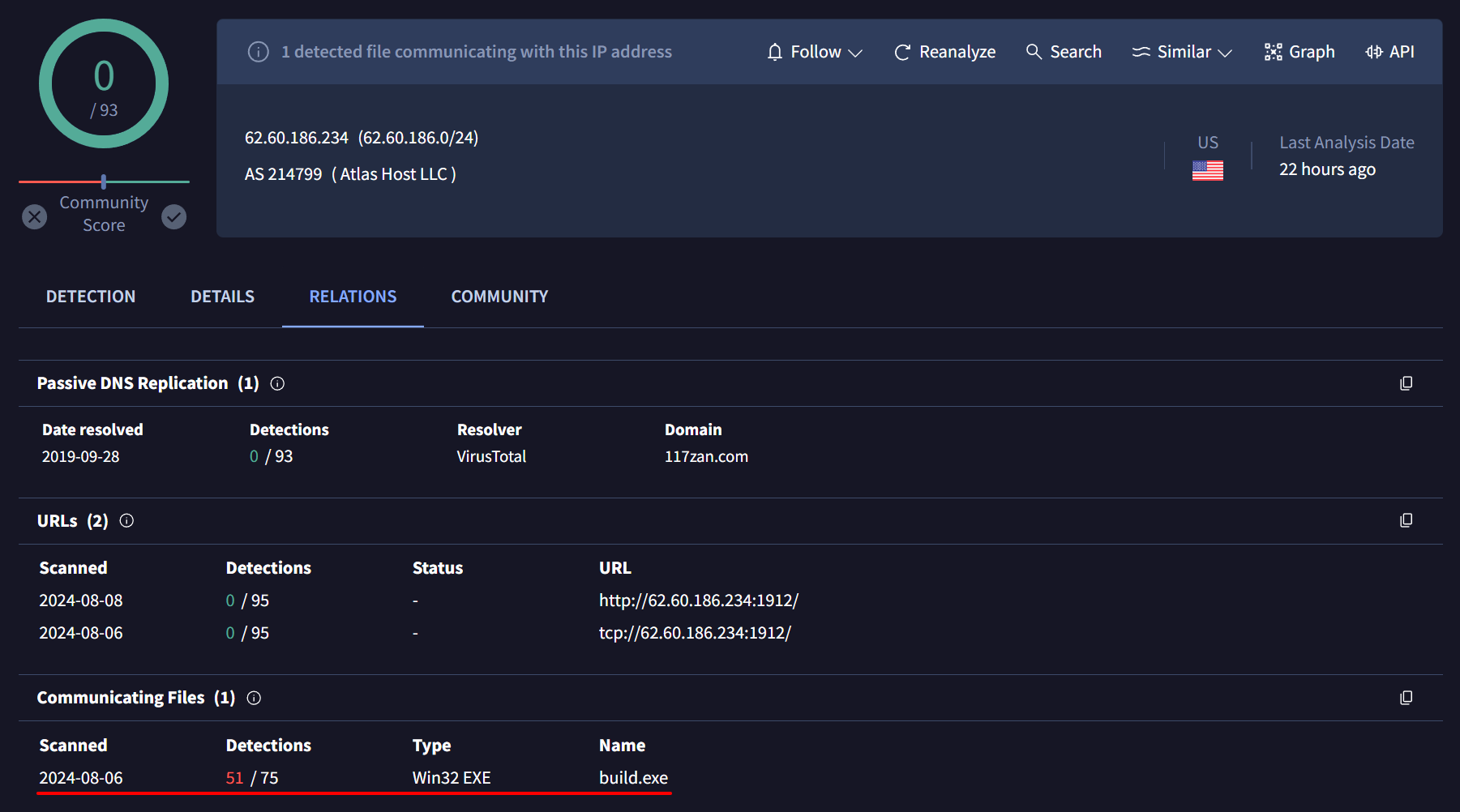
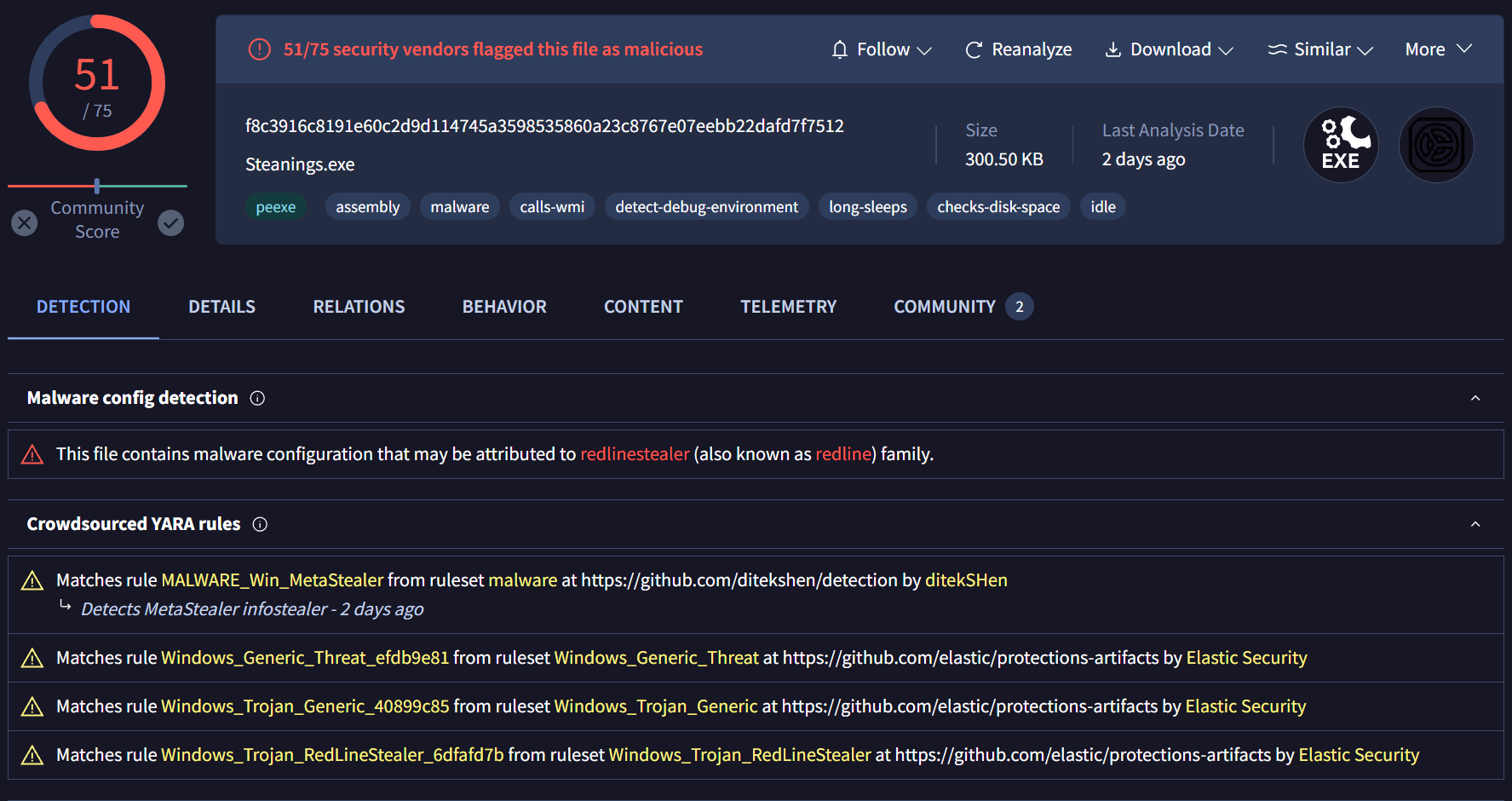
This connection suggests that the threat actors are using the same infrastructure to distribute different forms of malware, expanding their attack surface.
Conclusion
As we’ve explored, the Spynote Android malware was successfully injected into a seemingly legitimate Turbo VPN application, highlighting the dangers of using untrusted apps, especially in times of heightened demand, such as during Turkey’s recent Instagram ban. Interestingly, this isn’t the first time Spynote has been used to target unsuspecting users. In 2023, Kaspersky published an article titled “Gaming-related cyberthreats in 2023” where they detailed how Spynote was distributed among Roblox users on the Android platform under the guise of a game mod.
This connection is particularly relevant today, as Turkey also recently banned Roblox, potentially driving users to seek alternative methods of access, just as they did with Instagram. The parallel between these incidents underscores the need for heightened vigilance in digital security, especially when popular platforms become inaccessible, pushing users towards risky alternatives.
In conclusion, whether it’s through fake VPNs or malicious game mods, attackers are quick to exploit any opportunity to spread malware. Users should remain cautious, especially when downloading apps from unverified sources.
IOCs
1
2
5079208324c004d5ae538b48bbfdecdcf0a4e6542dcc283328d77e8398ab9f92
62.60.186.234:7771
References
- https://securelist.com/game-related-threat-report-2023/110960/
https://malpedia.caad.fkie.fraunhofer.de/details/apk.spynote
I utilized AI assistance to fine-tune certain sentences in this post, enhancing clarity and precision. The banner image was also created using AI.